According to the Mortgage News Daily, sale inventories have been slow to rebound from the Great Recession even
though home prices have increased steadily since 2012. Two Federal Reserve Bank
of San Francisco senior economists, William Hedberg and John Krainer theorize that prices are
still not high enough to entice many sellers.
For some this is because the value of their home is still below the
outstanding balance on their mortgage (also known as a negative amortization in mortgage parlance), meaning that sellers would have to bring
cash to the closing. For others it may
be that their equity is not back to a level that motivates them to sell.
Economic theory suggests that all homes are for sale if the price
is right, but at any point in time, the price may not be right. Sellers have
their own ideas about what is "right" and must also consider that selling a
house can be costly because of brokerage fees, and necessary or cosmetic
changes to the house. For these reasons
and others the active listing a home is viewed by economists as a strong signal
of an intent to sell and they measure the short-run supply of homes for sale,
the inventory, by the listing numbers.
Good times or bad, there is always some level of inventory in the housing
market. Some owners sell to move up,
others to downsize, other move for employment reasons, or to free up cash. These are life-cycles motives not necessarily
tied to the business cycle and produce a general level of churning in the
market. Nevertheless the authors say
there is a distinct cyclical pattern to inventories which rise in good times
and fall in bad times.
Credit conditions, which are also cyclical, can account for some of
this. Risk premiums charged by lenders
and their willingness to lend, tend to ease during good economic times, allowing
more potential buyers to enter the market. But it is the level of house prices
which is by far the variable that most influences the inventory of homes for
sale.
Even though not all listed homes are vacant Census Bureau data on the
numbers and price level of vacant homes have a long history of indicating the
relationship between inflation-adjusted house prices and for-sale inventory. As Figure 1 shows, inventories generally move
with prices and changes in house prices have a causal effect on inventories. The two series are tied together in a
long-run relationship and the authors say this makes sense as rising house
prices should encourage home owners to sell and thus inventories to rise.
 |
| Vacancies for sale over the years |
Inventories do not instantly react to house price changes and other
economics can disrupt the price/inventory relationship as is evident in the
most recent time period in the figure above.
House prices have been recovering broadly since 2012 but inventories
have been declining. Only recently have
they begun to rise.
The relationship between inventory and prices may have broken down for an
extended period as the market rebounded in 2012 because of fallout from the housing
boom and bust. The boom saw an unprecedented rise in
homeownership rates with younger households more willing to buy and eased lending
allowing in less qualified borrows. When
those trends reversed the inventory shifted from homes for sale to homes for
rent with the later rising steadily during the recession and the for-sale
inventory dropping and only recently stabilizing.
The authors say the data does not go back far enough to show if
this is a typical reaction but some Census Bureau data suggest it is unprecedented
since the 1960s. The phenomenon is
widespread and cannot be accounted for solely by the surge in
foreclosures. The inventory of homes in foreclosure
has recently been falling in most markets but the ratio of owner occupied and
renter occupied units has remained down. Thus, either preference for
home ownership has shifted or, more likely, credit constraints have affected
household home purchase decisions.
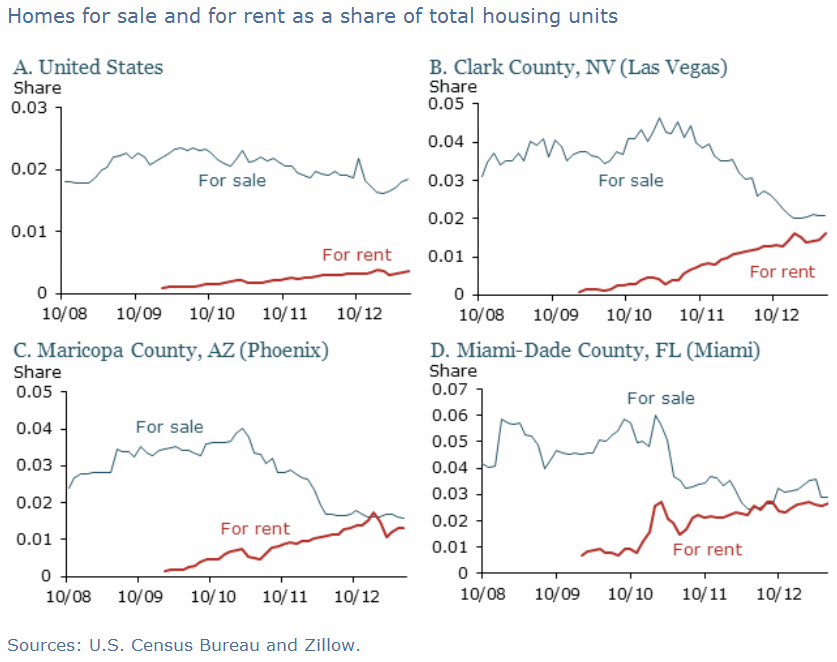
The changes in for-sale and for-rent inventories are seen most dramatically
in markets like Las Vegas, Phoenix and Miami where foreclosures were high and
investors have been buying large numbers of the foreclosed properties. In these market the total inventory of homes
for rent is approaching that of homes for sale, a remarkable shift that has
continued throughout the recovery. But,
in addition to the investor-effect the decline in homes for sale is very
closely linked with the large downward shift in the home ownership rate in these
markets. It is impossible to say though whether declining sales are pushing
down home ownership rates or falling home ownership is pushing down sales, or
both are interacting with each other in a complicated feedback process.
Tight credit conditions may be affecting both the ownership decisions of
young buyers and the supply side of the market.
In theory, falling house prices alone may keep some home owners from
selling. It may seem logical that decisions to sell should be based only on
information about current and future market conditions and the authors point to
research that shows home owners take more time to sell if home prices have
fallen since the original purchase. That is, two similar home owners
experiencing similar housing market conditions will behave differently if one
of those home owners has an unrealized loss on his or her house.
Falling prices may hold down home sales for several reasons. An underwater
home owner may be unwilling or unable to make up the difference between sale
proceeds and mortgage balance and chose to delay selling. Even if there is equity, it may be reduced
enough that no cash is available for the down payment on another home.
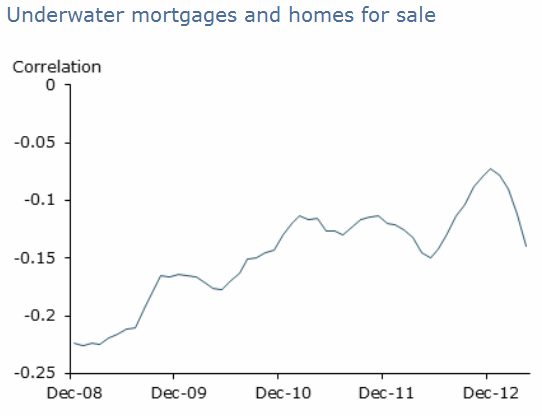
Since early 2008, homes for sale and homes underwater have been negatively
correlated. Counties with a high share
of underwater mortgages have tended to have smaller for-sale inventories. The authors say that while this relationship
is significant, its strength diminished as the recovery got under way.
Underwater borrowers may have been locked into their houses in a way that
impaired the normal functioning of the housing market. But that effect seems to
be waning.
Another explanation for this breakdown is that home owners may be
taking a longer view of the market. In
the housing cycle price changes are persistent, that is both price rises and
price drops are likely to be followed by more of the same. Home owners who can be flexible on timing a
sale can take advantage of this persistence, waiting and gambling that
increases will continue and they can sell at a higher price.
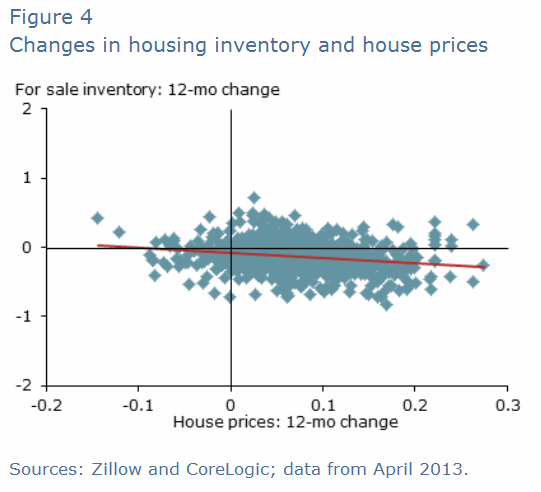
Figure 4 confirms on a county level the negative relationship between prices
and inventories shown at the aggregate level in Figure 1. Where counties
experienced relatively large price increases they also saw for-sale inventories
decline.
The authors say it turns out that that variables such as recent house price
appreciation and changes in employment are the most robust predictors of recent
changes in housing inventory. Once these are accounted for other variables,
such as changes in the for-rent inventory, the underwater share, or local
price-rent ratios, do little to explain the inventory of houses for sale. "Thus,
current home owners may be making a rational choice to postpone selling in the
hope that prices will rise further. However, this behaviour tends to be short
run. In the longer run, the link between the level of house prices and for-sale
inventories is strong. If prices continue to rise, inventories for sale should
eventually rise too."
Conclusion of the article:
History shows a long-run relationship between house prices and the number of
houses available for sale. Thus, current inventories of homes for sale are low
given more than a year of house price appreciation. County-level data suggest
that many home owners are waiting for prices to rise further in their markets.
Markets that have seen the strongest house price appreciation and job growth
are the ones where for-sale inventories have declined the most.
